Today, in the Huffington Post, I posted a document that shows an earlier incarnation of the ABACUS trade (although, not that different from the one that has got the SEC up in arms). I also explained it as well as I could. Head on over and let me know what you think.
Archive for the ‘Assets’ category
Inside Goldman’s ABACUS Trade
April 19, 2010Why 2010 will be Challenging for Goldman Sachs
December 30, 2009I figured I’d let 2009 go out with a bang and post another of my contrarian views: 2010 will be rough for Goldman Sachs. Why? Well, to know the answer to that, you should head on over to the Huffington Post where the full piece is online.
Happy New Year!
Revisiting a Debate We Should be Past
June 10, 2009Recently, Felix Salmon, Clusterstock, and others have been mentioning an essay from the Hoover Institute about the financial crisis. Now, I haven’t yet linked to the essay in question… I will, but only after I’ve said some thing about it.
I was on the front lines of the securitization boom. I saw everything that happened and am intimately familiar with how one particular bank, and more generally familiar with many banks’, approach to these businesses. I think that there are no words that adequately describes how utterly stupid it is that there is still a “debate” going on surrounding banks and their roles in the financial crisis. There are no unknowns. People have been blogging, writing, and talking about what happened ad naseum. It’s part of the public record. Whomever the author of this essay is (I’m sure I’ll be berated for not knowing him like I was for not knowing Santelli — a complete idiot who has no place in a public conversation whose requisites are either truth or the least amount of intellectual heft), unless it’s writing was an excesses in theoretical reasoning about a parallel universe, it’s a sure sign they don’t what they are talking about that they make some of the points in the essay. Let’s start taking it apart so we can all get on with our day.
For instance, it isn’t true that Wall Street made these mortgage securities just to dump them on them the proverbial greater fool, or that the disaster was wrought by Wall Street firms irresponsibly selling investment products they knew or should have known were destined to blow up. On the contrary, Merrill Lynch retained a great portion of the subprime mortgage securities for its own portfolio (it ended up selling some to a hedge fund for 22 cents on the dollar). Citigroup retained vast holdings in its so-called structured investment vehicles. Holdings of these securities, in funds in which their own employees personally participated, brought down Bear Stearns and Lehman Brothers. AIG, once one of the world’s most admired corporations, made perhaps the biggest bet of all, writing insurance contracts against the potential default of these products.
So Wall Street can hardly be accused of failing to eat its own dog food. It did not peddle to others an investment product that it was unwilling to consume in vast quantities itself.
(Emphasis mine.)
Initial premise fail. I had a hard time finding the part to emphasize since it’s all so utterly and completely wrong. Since I saw everything firsthand, let me be unequivocal about my remarks: the entire point of the securitization business was to sell risk. I challenge anyone to find an employee of a bank who says otherwise. This claim, that “it isn’t true that Wall Street made these mortgage securities just to dump them on them the proverbial greater fool” is proven totally false. There’s a reason the biggest losers in this past downturn were the biggest winners in the “league tables” for years running. As a matter of fact, there’s a reason that league tables, and not some other measure, were a yardstick for success in the first place! League tables track transaction volume–do I really need to point out that one doesn’t judge themselves by transaction volume when their goal isn’t to merely sell/transact?
In fact, the magnitude of writedowns by the very firms mentioned (Merrill and Citi) relative to the original value of these investments imply that a vast, vast majority of the holdings were or were derived from the more shoddily underwritten mortgages underwritten in late 2006, 2007, and early 2008. In fact, looking at ABX trading levels, as of yesterday’s closing, shows the relative quality of these mortgages and makes my point. AAA’s from 2007 (series 1 and 2) trading for 25-26 cents on the dollar and AAA’s from early 2006 trading at roughly 67 cents on the dollar. The relative levels are what’s important. Why would Merrill be selling it’s product for 22 cents on the dollar if the market level is so much higher (obviously the sale occurred a few months ago, but the “zip code” is still the same)? This is a great piece of evidence that banks are merely left holding the crap they couldn’t sell when the music stopped.
Now, onto the next stop on the “How wrong can you get it?” tour.
It isn’t true, either, that Wall Street manufactured these securities as a purblind bet that home prices only go up. The securitizations had been explicitly designed with the prospect of large numbers of defaults in mind — hence the engineering of subordinate tranches designed to protect the senior tranches from those defaults that occurred.
Completely incorrect. Several people who were very senior in these businesses told me that the worst case scenario we would ever see was, perhaps, home prices being flat for a few years. I never, not once, saw anyone run any scenarios with home price depreciation. Now, this being subprime, it was always assumed that individuals refinancing during the lowest interest rate period would start to default when both (a) rates were higher and (b) their interest rates reset. [Aside: Take note that this implicitly shows that people running these businesses knew that people were taking out loans they couldn’t afford.] Note that the creation of subordinate tranches, which were cut to exactly match certain ratings categories, was to (1) fuel the CDO market with product (obviously CDO’s were driven by the underlying’s ratings and were model based), (2) allow AAA buyers, including Fannie and Freddie, an excuse to buy bonds (safety!), and (3) maximize the economics of the execution/sale/securitization. If there were any reasons for tranches to be created, it had absolutely nothing to do with home prices or defaults.
Further, I would claim that there wasn’t even this level of detail applied to any analysis. We’ve seen the levels of model error that are introduced when one tries to be scientific about predictions. As I was told many times, “If we did business based on what the models tell us we’d do no business.” Being a quant, this always made me nervous. In retrospect, I’m glad my instincts were so attuned to reality.
As a matter of fact, most of the effort wasn’t on figuring out how to make money if things go bad or protect against downside risks, but rather most time and energy was spent reverse engineering other firm’s assumptions. Senior people would always say to me, “Look, we have to do trades to make money. We buy product and sell it off–there’s a market for securities and we buy loans based on those levels–at market levels.” These statements alone show how singularly minded these executives (I hate that term for senior people) and businesses were. The litmus test for doing risky deals wasn’t ever “Would we own these?” it was “Can we sell all the risk?”
But wait, there’s more…
Nor is it plausible that all concerned were simply mesmerized by, or cynically exploitive of, the willingness of rating agencies to stamp Triple-A on these securities. Wall Street firms knew what the underlying dog food consisted of, regardless of what rating was stamped on it. As noted, they willingly bet their firm’s money on it, and their own personal money on it, in addition to selling it to outsiders.
One needs the “willingly bet [their own] money on it” part to be true to make this argument. I know exactly what people would say, “We provide a service. We aggregate loans, create bonds, get those bonds rated, and sell them at the levels the market dictates. It isn’t our place to decide if our customers are making a good or bad investment decision.” I know it’s redundant with a lot of the points above, but that’s life–the underlying principles show up everywhere. And, honestly, it’s the perfect defense for, “How did you ever think this made sense?”
And, the last annoying bit I read and take issue with…
Nor is it true that Wall Street executives and CEOs had insufficient “skin in the game,” so that “perverse” compensation incentives created the mess. That story also does not pan out. Individuals, it’s true, were paid sizeable bonuses in the years in which the securities were created and sold.
[…]
Richard Fuld, of failed Lehman Brothers, saw his net worth reduced by at least a hundred million dollars. James Cayne of Bear Stearns was reported to have lost nearly a billion dollars in a matter of a few months. AIG’s Hank Greenberg, who remained a giant shareholder despite being removed from the firm he built by New York Attorney General Eliot Spitzer in 2005, lost perhaps $2 billion. Thousands of lower-downs at these firms, those who worked in the mortgage securities departments and those who didn’t, also saw much wealth devastated by the subprime debacle and its aftermath.
Wow. Dick Fuld, who got $500 million, had his net worth reduced by $100 million? That’s your defense? And, to be honest, if you can’t gin up this discussion, then what can you gin up? The very nature of this debate is that all of these figures are unverifiable. James Cayne was reported to have lost nearly a billion dollars? Thanks, but what’s your evidence? The nature of rich people is that they hide their wealth, they diversify, and they skirt rules. So, sales of stock get fancy names like prepaid variable forwards. Show me their bank statements–even silly arguments need a tad of evidence, right?
Honestly, at this point I stopped reading. No point in going any further. So, now that you know how little regard for that which is already known and on the record this piece of fiction is, I’ll link to it…
Although, Felix does a great job of taking this piece down too (links above)… Although, he’s a bit less combative in his tone.
Nor is it plausible that all concerned were simply mesmerized by, or cynically exploitive of, the willingness of rating agencies to stamp Triple-A on these securities. Wall Street firms knew what the underlying dog food consisted of, regardless of what rating was stamped on it.
Guest Post at Clusterstock
April 23, 2009Hey, I wanted to let you, my loyal readers, know that I guest posted over at Clusterstock. The post, entitled “Investment Bank Scorecard” is my take on this past quarter as a whole. I think it’s worth clicking over and taking a look. I’d sum it up here, but, in all honesty, the value is in the nuances and small insights more than the general thesis.
Also, here is the chart attached to that post, in its orginal form.
Repaying T.A.R.P.: There Are Restrictions
April 21, 2009There is a meme (did you know that word was invented by Richard Dawkins?) going around the blogosphere that, in essence, says Geithner doesn’t have the right to prevent T.A.R.P. repayment, even if no fresh capital is raised. This is incorrect. From the Goldman Sachs T.A.R.P. agreements [pdf!] governing the capital infusion (it’s hidden on the site, but there!):

(Emphasis [yes, that’s the green underlining] mine.)
Seems, then, that it’s pretty clear. Whole or partial payments, once allowed by a regulator, require fresh equity raised from a “Qualified Equity Offering.” This is a defined term, and the document defines it as follows:

So, it seems pretty cleat that there are conditions. Now, maybe these aren’t the systemic considerations, but that’s likely why the regulatory approval is required, especially in conjunction with the “stress test,” which we’ve discussed here at length.
Citi’s Earnings: Even Cittier Than You Think
April 20, 2009Well, Citi reported earnings this past week. And, as many of you know, there are a few reasons you’ve heard to be skeptical that this was any sort of good news. However, there are a few reasons you probably haven’t heard… (oh, and my past issues on poor disclosure are just as annoying here)
On Revenue Generation: First, here are some numbers from Citi’s earnings report and presentation, Goldman’s earnings report, and JP Morgan’s earnings report:

These numbers should bother Citi shareholders. Ignoring the 1Q08 numbers, Citi–whose global business is much larger and much more diverse than it’s rivals–generates no more, if not slightly less, revenue than the domestically focused JP Morgan and much, much less than Goldman. But it gets worse. Goldman’s balance sheet was $925 billion vs. Citi’s $1.06 trillion in assets within it’s investment banking businesses, roughly 10% larger. I’d compare JP Morgan, but they provide a shamefully small amount of information. As an entire franchise, however, Citi was able to generate their headline number: $24.8 billion in revenue, on assets of $1.822 trillion. JP Morgan, as a whole, was able to generate $26.9 billion, on assets of $2.079 trillion. JP Morgan, then is 14% larger, by assets, and generstes 8% higher revenue.
These numbers should be disconcerting to Citi, it’s no better at revenue generation than it’s rivals, despite having a larger business in higher growth, higher margin markets. Further, in an environment rife with opportunity (Goldman’s results support this view, and anecdotal support is strong), Citi was totally unable to leverage any aspect of it’s business to get standout results… and we’re only talking about revenue! Forget it’s cost issues, impairments and other charges as it disposes assets, etc.
On The Magical Disappearing Writedowns: Even more amazing is the lack of writedowns. However, this isn’t because there aren’t any. JP Morgan had writedowns of, approximately, $900 million (hard to tell, because they disclose little in the way of details). Goldman had approximately $2 billion in writedowns (half from mortgages). Citi topped these with $3.5 billion in writedowns on sub-prime alone (although they claim only $2.2 billion in writedowns, which seems inconsistent). But, that isn’t close to the whole story. Last quarter, in what I could find almost no commentary on during the last conference call and almost nothing written about in filings or press releases, Citi moved $64 billion in assets from the “Available-for-sale and non-marketable equity securities” line item to the “Held-to-maturity” line item. In fact, $10.6 billion of the $12.5 billion in Alt-A mortgage exposure is in these, non–mark-to-market accounts. There was only $500 million in writedowns on this entire portfolio, surprise! Oh, and the non–mark-to-market accounts carry prices that are 11 points higher (58% of face versus 47% of face). What other crap is hiding from the light? $16.1 billion out of $16.2 billion total in S.I.V. exposure, $5.6 billion out of $8.5 billion total in Auction Rate Securities exposure, $8.4 billion out of $9.5 billion total in “Highly Leveraged Finance Commitments,” and, seemingly, $25.8 billion out of $36.1 billion in commercial real estate (hard to tell because their numbers aren’t clear), are all sitting in accounts that are no longer subject to writedowns based on fluctuations in market value, unlike their competitors. These are mostly assets managed off the trading desk, but marked according to different rules than traded assets. If one doesn’t have to mark their assets, then having no writedowns makes sense.
On The Not-so-friendly Trend: This is a situation where, I believe, the graphs speak for themselves.



Do any of these graphs look like things have turned the corner? Honestly, these numbers don’t even look like they are decelerating! Compare this with the (relatively few) graphs provided by JP Morgan.



These aren’t directly comparable, as the categories don’t correspond to one another, and JP Morgan uses the more conservative 30-day delinquent instead of Citi’s 90+-day delinquent numbers. However, JP Morgan’s portfolio’s performance seems to be leveling out and even improving (with the possible exception of “Prime Mortgages”). Clearly, the pictures being painted of the future are very different for these institutions.
On the Stuff You Know About: I’ll be honest, this business about Citi benefiting from it’s own credit deterioration was confusing. Specifically, there is more going on when Citi refers to “credit value adjustments” than just profiting from it’s own Cittieness. However, Heidi Moore, of Deal Journal fame helped set me straight on this–the other things going on are dwarfed by the benefit I just mentioned. Here’s the relevant graphic from the earnings presentation:

And, via Seeking Alpha’s Transcript, the comments from Ned Kelly that accompanied this slide:
Slide five is a chart similar to one that we showed last quarter which shows the movement in corporate credit spreads since the end of 2007. During the quarter our bond spreads widened and we recorded $180 million net gain on the value of our own debt for which we’ve elected the fair value option. On our non-monoline derivative positions counterparty CDS spreads actually narrowed slightly which created a small gain on a derivative asset positions.
Our own CDS spreads widened significantly which created substantial gain on our derivative liability positions. This resulted in a $2.7 billion net mark to market gain. We’ve shown on the slide the five-year bond spreads for illustrative purposes. CVA on our own fair value debt is calculated by weighting the spread movements of the various bond tenors corresponding to the average tenors of debt maturities in our debt portfolio. The debt portfolio for which we’ve elected the fair value options is more heavily weighted towards shorter tenures.
Notice that Citi’s debt showed a small gain, but it’s derivatives saw a large gain (the additional $166 million in gains related to derivatives was due to the credit of it’s counterparties improving). Why is this? Well, notice the huge jump in Citi’s CDS spread over this time period versus cash bonds, which were relatively unchanged. Now, from Citi’s 2008 10-K:
CVA Methodology
SFAS 157 requires that Citi’s own credit risk be considered in determining the market value of any Citi liability carried at fair value. These liabilities include derivative instruments as well as debt and other liabilities for which the fair-value option was elected. The credit valuation adjustment (CVA) is recognized on the balance sheet as a reduction in the associated liability to arrive at the fair value (carrying value) of the liability.
Citi has historically used its credit spreads observed in the credit default swap (CDS) market to estimate the market value of these liabilities. Beginning in September 2008, Citi’s CDS spread and credit spreads observed in the bond market (cash spreads) diverged from each other and from their historical relationship. For example, the three-year CDS spread narrowed from 315 basis points (bps) on September 30, 2008, to 202 bps on December 31, 2008, while the three-year cash spread widened from 430 bps to 490 bps over the same time period. Due to the persistence and significance of this divergence during the fourth quarter, management determined that such a pattern may not be temporary and that using cash spreads would be more relevant to the valuation of debt instruments (whether issued as liabilities or purchased as assets). Therefore, Citi changed its method of estimating the market value of liabilities for which the fair-value option was elected to incorporate Citi’s cash spreads. (CDS spreads continue to be used to calculate the CVA for derivative positions, as described on page 92.) This change in estimation methodology resulted in a $2.5 billion pretax gain recognized in earnings in the fourth quarter of 2008.
The CVA recognized on fair-value option debt instruments was $5,446 million and $888 million as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The pretax gain recognized due to changes in the CVA balance was $4,558 million and $888 million for 2008 and 2007, respectively.
The table below summarizes the CVA for fair-value option debt instruments, determined under each methodology as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the pretax gain that would have been recognized in the year then ended had each methodology been used consistently during 2008 and 2007 (in millions of dollars).
Got all that? So, Citi, in it’s infinite wisdom, decided to change methodologies and monetize, immediately, an additional 290 bps in widening on it’s own debt. This change saw an increase in earnings of $2.5 billion prior to this quarter. In fact, Citi saw a total of $4.5 billion in earnings from this trick in 2008. However, this widening in debt spreads was a calendar year 2008 phenomenon, and CDS lagged, hence the out-sized gain this quarter in derivatives due to FAS 157 versus debt. Amazing.
And, while we’re here, I want to dispel a myth. This accounting trick has nothing to do with reality. The claim has always been that a firm could purchase it’s debt securities at a discount and profit from that under the accounting rules, so this was a form of mark-to-market. Well, unfortunately, rating agencies view that as a technical default–S&P even has a credit rating (“SD” for selective default) for this situation. This raises your cost of borrowing (what’s to say I’ll get paid in full on future debt?) and has large credit implications. I’m very, very sure that lots of legal documents refer to collateral posting, and other negative effects if Citi is deemed in “default” by a rating agency, and this would be a form of default. This is a trick, plain and simple–in reality, distressed tender offers would cost a firm money.
The Bottom Line: Citi isn’t out of the woods. In this recent earnings report I see a lot of reasons to both worry and remain pessimistic about Citi in the near- and medium-term. If you disagree, drop me a line… I’m curious to hear from Citi defenders.
Exclusive Breaking News: Newspapers to Receive Massive Capital Infusion
March 31, 2009Through some contacts in the banking industry I have obtained a draft of a news story that is expected to be run tomorrow. This is clearly newsworthy and I’m proud that something this important is the first news story ever to be broken by this blog. The full text of the story is below.
——
Newspaper Industry gets Large Capital Infusion
New York (AFD Wire) — Newspaper companies have “agreed in principle” on a deal to receive a $15 billion capital infusion over the next two years from a consortium of organizations focused on the pet industry. While the transaction details aren’t final yet, The Cat Fanciers Association, American Kennel Club, and the American Pet Products Association are expected to requested a one-time “emergency fee” from all members, totaling $5 billion, and will increased their dues and other membership fees to payout the remaining $10 billion quarterly over the next two years.
When called for a comment James Whittier, head of the American Kennel Club, who lead the negotiations on behalf of the pet industry, confirmed the talks and made the following statements regarding the transaction: “We have and have always had a strong bond with the newspaper industry. Before today we were emotionally and professionally invested in it’s survival–today, we will be announcing a financial investment as well. Without newspapers and their vital use in the housebreaking process there would be a massive oversupply of puppies and kittens without loving homes. Without newspapers it would be all-but-impossible for working individuals to own all but the strongest bladdered pets.”
John Exeter Ecstrum, or “Extra Extra” as he’s known to colleagues, lead the discussions on behalf of the newspaper industry. Mr. Ecstrum is a retired newspaper executive who has served as a director for The New York Times Co. (NYSE: NYT), the Newspaper Association of America, and various private news and publishing companies. Mr Ecstrum, via his public relations team released a statement: “To show how strong the bond between the pet industry and the newspaper industry has become, our trade groups estimate that around 75% of physical newspapers are purchased for non-human use, up from just 30% ten years ago. This demonstrates the fastest growing segment of our business and we’re proud to strengthen and formalize that relationship with today’s announcement. This transaction showcases another example of websites, blogs, and online-only news failing to deliver the same service and usefulness as print news.”
Notably absent from the detailed list of participating organizations was the Westminster Kennel Club, the organization responsible for the the annual Westminster Kennel Club Dog Show. Ms. Margaret Ames Steubenpfoffer, IV, president of Westminster Corp., parent company of the Kennel Club, noted, “The club has very strict rules relating to the care of dogs that compete in our shows. Ever since 1995 we have required show dogs’ leavings be deposited on squares no smaller than three feet by three feet cut from bolts of low-grade silk.” Ms. Steubenpfoffer repeatedly re-iterated that using “newsprint” was inappropriate and degraded the quality of the living environment champion dogs required.
Parties close to the negotiations expect the details to be finalized this afternoon and a formal announcement of the specific terms, along with a draft agreement, to be released.
Why Stress Test Really Means Guesswork
March 15, 2009Well, we’ve heard a ton about stress tests recently. Want some details on what a stress test entails? The Journal has some details about the tests here. Now, as much as I think GDP and unemployment are fine things to project forward for economists, let’s walk through the way one would use this to actually price an asset. Let’s start with something simple, like a 10-year treasury note (note that treasury bond specifically refers to bonds with a 30-year maturity). Here are all the components one would need to stress test the value of a treasury note.
- Characteristics of the note itself: coupon, payment dates, maturity dates, etc.
- What the yield curve would look like at the date you’re pricing the note.
Why would one need to know the shape of the yield curve (term structure of rates)? This is important, in order to “PV” the bond’s cashflows most accurately, one would discount each cashflow by it’s risk–the simplest proxy is to discount each cash flow by the rate of interest one would need to pay to issue a bond maturing on that date. For the government, this rate of interest is the point on the treasury yield curve (actually, the par zero curve) with the same maturity date. An example would be, if I were going to price a cash payment I will receive in two years, and the government can currently issue two-year debt at 5%, I should discount my cash payment (also from the government, since it’s a treasury note) at 5%. Treasuries are the simplest of all instruments to value.
Here’s an example, form the link above, of what a treasury yield curve might look like:
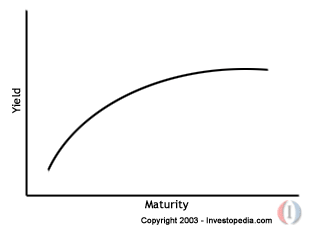
Now, it is completely and totally guesswork to figure out, given unemployment and GDP figures, what the yield curve will look like at any date in the future. Indeed, one can plug these projections into a model and it can come up with a statistical guess… But the only thing we know for sure about that guess is that it won’t be accurate, although it might be close. However, things like inflation will drive the longer end of the yield curve and monetary policy will drive the shorter end, so these certainly aren’t directly taken from the stress test parameters, but would need to be a guess based on those parameters. This is a large source of uncertainty in pricing even these instruments in the stress test.
Next, let’s examine a corporate bond. What would we need for a corporate bond?
- Characteristics of the bond: coupon, payment dates, maturity dates, special features (coupon steps, sinking funds, call schedules, etc.), where in the capital structure this bond sits, etc.
- What the yield curve would look like at the date you’re pricing the bond.
- The spreads that the corporation’s debt will carry at the date you’re pricing the bond.
Oh no. We already saw the issues with #2, but now we have #3. What will this corporations credit spread (interest/yield required in excess of the risk free rate) at the time of pricing? Will the corporations debt, which could trade at a spread of anywhere from 5 to 1500 basis points, be lower? higher? Will the corporations spread curve be flatter? steeper?
Here is a good illustration of what I’m referring to (from the same source as the figure above):

There, the spread is the difference between the purple line and the black line. As you can see, it’s different for different maturity corporate bonds (which makes sense, because if a company defaults in year two, it’ll also default on it’s three year debt.. but the companies’ two year debt might never default, but the company might default during it’s third year, creating more risk for three year bonds issued by that company than two year bonds). It shouldn’t be a surprise, after our exercise above, to learn that the best way to compute the price of a corporate bond is to discount each cashflow by it’s risk (in my example above, regardless of whether the company defaults in year two or year three, the interest payments from both the three year and two year debt that are paid in one year have the same risk).
Well, how does one predict the structure of credit spreads in the future? Here’s a hint: models. Interest rates, however, are an input to this model, since the cost of a firm’s borrowing is an important input to figuring out a corporation’s cashflow and, by extension, creditworthiness. So now we have not only a flawed interest rate projection, but we have a projection of corporate risk that, in addition to being flawed itself, takes our other flawed projections as an input! Understanding model error yet? Oh, and yes unemployment and the health of the economy will be inputs to the model that spits out our guess for credit spreads in the future as well.
Next stop on the crazy train, mortgage products! What does one need to project prices for mortgage products?
- Characteristics of the bond: coupon, payment dates, maturity dates, structure of the underlying securitization (how does cash get assigned in the event of a default, prepayment, etc.), etc.
- What the yield curve would look like at the date you’re pricing the bond.
- The spreads that the debt will carry at the date you’re pricing the bond.
- What prepayments will have occurred by the date you’re pricing the bond and what prepayments will occur in the future, including when each will occur.
- What defaults will have occurred by the date you’re pricing the bond and what defaults will occur in the future, including when each will occur.
Oh crap. We’ve covered #1-3. But, look at #4 and #5 … To price a mortgage bond, one needs to be able to project out, over the life of the bond, prepayments and defaults. Each is driven bydifferent variables and each happens in different timeframes. Guess how each projection is arrived at? Models! What are the inputs to these models? Well, interest rates (ones ability to refinance depends on where rates are at the time) over a long period of time (keep in mind that you need rates over time, having rates at 5% in three years is completely different if rates where 1% or 15% for the three years before). General economic health, including regional (or more local) unemployment rates (if the south has a spike in unemployment, but the rest of the country sees a slight decrease, you’ll likely see defaults increase). And a myrid of other variables can be tossed in for good measure. So now we have two more models, driven by our flawed interest rate projections, flawed credit projections (ones ability to refinance is driven by their mortgage rate, which is some benchmark interest rate [treasuries here] plus some spread, from #3), and the unemployment and GDP projections.
I will, at this point, decline to talk about pricing C.D.O.’s … Just understand, however, that C.D.O.’s are portfolios of corporate and mortgage bonds, so they are a full extra order of magnitude more complex. Is it clear, now, why these stress tests, as they seem to be defined, aren’t all that specific, and potentially not all that useful?
How to Fix the Crisis in Six Easy Steps
February 26, 2009There is a lot of chatter about different plans, market anticipations, and pitfalls when it comes to “fixing” the economy and, specifically, nationalization. Despite the fact that I don’t have the same reach as several uneducated members of the media, I figured I’d share what I think the way forward is, regardless.
Step 1: Nationalize Citi and Bank of America. Let’s be honest, with recent talks of expanded stakes, ringfenced assets, and no end of the losses in sight, it’s probably time the U.S. Government came to grips with the fact that they already own the losses and the positive impact of letting shareholders keep the upside is nonsensical. Further, these institutions will need more money for a long time to come. And, if you’re paying attention, you know that the markets seem to twist and turn with the news coming out of financial institutions. Nationalization rumors depress the markets, talks of further government action scare away new capital, and the fundamental health of these firms makes current investors run.
Step 2: Begin lending. With so much chatter and anger about institutions not lending, it almost makes me wonder why there is such a deep lack of understanding. These sick institutions are trying to shrink their balance sheets and have a ton of souring assets on them. They have to raise capital to support their current asset base, so why do we really expect these banks and other firms to lend? Some would claim that lending for the sake of lending got us into this mess, but they are either telling only part of the story or don’t get it–excessive leverage and poor risk management got us to this point. In fact, I suspect that defaults on even the riskiest loans would be much lower if bank capital was free enough to continue making mortgage loans based on normal requirements for returns and risk/reward.
So, how do we begin lending? Simple, start a government bank. Well, not exactly, but the government now owns Fannie, Freddie, AIG, Citi, and BofA (see step 1). Clearly the government now (by step 2) has the infrastructure and technical know-how to manage the logisitical issues of setting up and running a lending platform. Now the government can lend directly and not wait for sick banks to do it. Further, they can underwrite to fairly normal lending standards and get a premium return on their capital. Also, rather than poaching the nationalized entitites’ “talent,” the government cam employ many out of work finance workers throughout the country (after all, lending in Missouri should probably be done by people in Missouri).
Step 3: Begin replenishing bank assets with new, cleaner assets. With all of these souring assets on the books of banks, their capital base being eroded, and leverage decreasing, TARP capital is probably being deployed very inefficiently and, obviously, conservatively. Well, since step 2 involves lending and creating assets, the government should then implement an auction process–all assets the government creates would then be auctioned off, much like treasury bonds are, to banks. Since the government would be lending based on normal underwriting standards (as compared to the previous paradigm of loan underwriting), these assets would have a strong credit profile and will likely perform much better than legacy assets. JP Morgan, for example, should jump at the chance to generate higher levels of retained earnings by buying assets when the rates it needs to pay are at historically low levels, once its capital frees up. This solves the chicken-and-egg problem of curing sick banks, hurting from consumer defaults and depressed economic activity, to free up the credit markets and getting economic activity to increase despite a lack of credit.
One could easily permute this plan in many ways. One possible way is to offer to swap new assets for legacy assets at current market levels to facilitate a much more immediate strengthening of the banks’ balance sheets. Another variation could include some partial government guarentee on assets it originates. I’m sure there are thousands more ways one could add bells and whistles.
Step 4: Broaden the Fannie and Freddie loan modifications and housing stabilization plan to the government’s new properties. I suppose this should be some sort of addendum to step 1, but it’s important enough to require some emphasis on it’s own. With Citi and Bank of America being so large, I’m sure the housing stabilization plan will have a much broader reach once those are wards of the state. We’ve all heard the arguments for stopping foreclosures and refinancing borrowers… When the house next door is foreclosed upon, your house loses tens of thousands of dollar in value, increases housing supply, etc.
Step 5: Break up the institutions that are owned by the government. Markets have been clamoring for Citi to be broken up for years. Bank of America shareholders probably want Merrill to be broken off A.S.A.P. (ditto for Countrywide). Chew up these mammoth institutions and spit out pieces that, in the future, could fail because they aren’t too big. This should be done to AIG, Citi, Bank of America, and both Fannie and Freddie.
Step 6: Immediately implement a new regulatory regime. This is pretty much a “common sense measure.” President Obama has begun to call for this, and it’s pretty clear that with no more major investment banks around, the S.E.C.’s role needs to be re-defined. I’ve already laid out my thoughts on what this new structure should look like.
Between all of these steps, we should have the tainted institutions out of the system, credit will start to free up, banks asset base will become more reliable, and systemic risks will go down as we significantly decrease the number of firms that are “too big to fail.” Seems logical to me…


